
Save Money with Business Name Registration, Australia
Save Money with Business Name Registration, Australia
Save Money with Business Name Registration
You may be using a third party provider to keep your business name registrations up to date, but registering your business name directly through ASIC yourself may be the cheapest option and provide you with more certainty and control.
You can register for an ASIC Connect account, or you can use the ASIC business registration system.
If the website you are using to register a business name doesn’t include .gov.au in the domain name, then you will be paying extra to use the service. In 2022, you can register a business name directly with ASIC for just $39 per year, or $92 for 3 years.
Once registered, provided you keep your contact details up to date, you will receive notice of renewal from ASIC before your registration expires. If you discover that your registration has expired, then you will still have 30 days after the registration date to apply to re-register that name before it becomes available to the public.
If you receive letters from third party registration providers, they will usually be looking for annual fees that are more than what you would pay ASIC. Their additional fees cover the cost of their operations and their profits. ASIC publishes a list of what third party providers can and cannot do and you can complain to the provider if you have any concerns.
You should definitely NOT be paying more than one third party provider for registration services of the same name, and NOT for registration of your own name.
Do I Need An ABN To Register A Business Name?
Yes, you need an ABN to register a business name.
An ABN is an Australian Business Number, and it is attached to whatever entity you use to conduct your business, whether that is as a sole trader, through a trust, or as a company or incorporated association.
For people setting up private foundations who think they don’t need an ABN – check here.
Do I Need To Register My Company Name As A Business Name?
No.
If your company name is the same as the name of your business, then you don’t need to register them separately.
If you register a business name, no one will be able to register a company with the exact same name, and when you register your company name, no one will be able to register exactly the same name as a business name.
On the other hand, if you want to have separate business divisions with different names under the same company, then you can register multiple business names and, through your company ABN, they will be linked to your company, even though the company and the businesses have different names.
Sole traders can register multiple business names consistent with the different areas of business they are involved in. Those business names will be linked to their sole trader ABN.
Be aware that some third party providers will write to you encouraging you to register your business name without checking to see if you have changed your business structure and set up a company with the same name. Their interest is in receiving your payment for registration, whether or not it is required.
Do All Business Names Need To Be Registered?
Yes, and No.
Under the Business Names Registration Act 2011 (Federal), it is an offence to carry on a business under a name that is not registered. The penalty is 30 penalty units, which in 2022 equates to about $6,660. Doesn’t seem worth risking when its only $39 per year to register, does it?
Did you know you can be fined $6,660 for carrying on business without registering your business name?
If you use your personal name as a business name with a description of what you do – eg. “Emma Lee Accounting”, or “Sanjay Singh Consultants”, then you don’t need to register it, as using your own personal name for your business is not an offence. The same goes for a company that uses the company name to operate a business.
How Do You Check If A Name Is Taken For A Business?
Business name availability is easy to check, and a quick check can save you lots of money in the future.
The first thing you should do is complete a quick Google or other browser search on your chosen name. If you find a competitor in the same country with the same or a very similar name – go back to the drawing board. It’s not worth the hassle and you create the risk of having someone send you nasty legal letters telling you to stop using that name.
Secondly, complete a trade mark search. In Australia, you complete a trade mark search through IP Australia. If someone has a registered trade mark in broadly the same area of business as you, you risk getting a nasty legal letter telling you to stop using that name. The Onyx Legal team can help you assess whether or not you have any concerns about a registered trade mark, or would like to register your business name as a trade mark. Simply send us an email to advice@onyx.legal with “Trade Mark Registration enquiry” in the subject line and we will respond to your promptly.
Thirdly, and now that you are reasonably certain no one else has a name the same or very similar to what you want to use, then do a name availability check on ASIC. Select “Organisation and Business Names” then complete some or all of the words you want to use in the “Name or Number” field and select “Go”.
A list of Organisation and Business Names should appear. If there are more than 10 names, there will be multiple pages. You can change the settings to display up to 50 names at a time. When looking at names, anything that says “Registered” next to it in the “Status” column is not available to you.
For example, we searched “forthright”, which produced 20 results. 10 of those results are registered. In the “type” column, you can identify whether they are business names or company names.
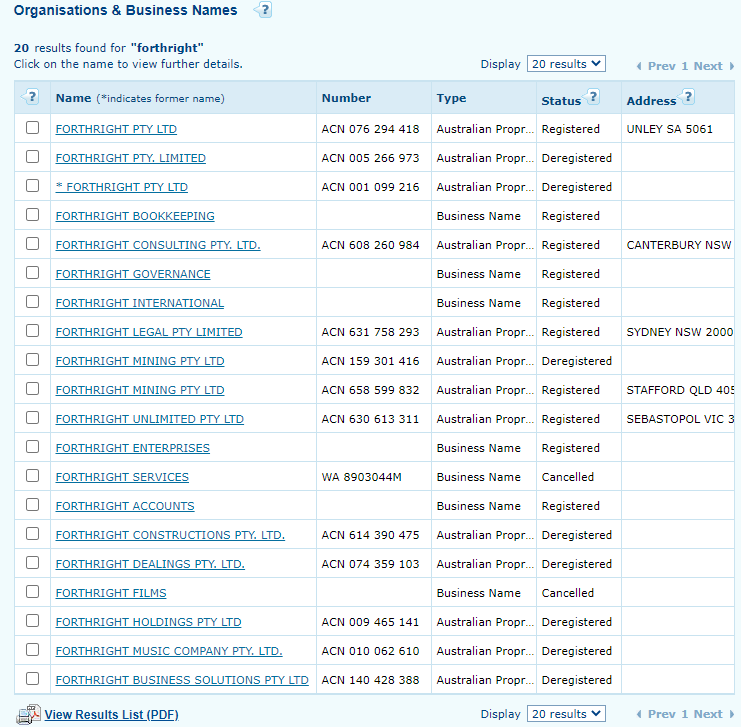
You won’t be able to register a business name if it is already being used by a company, and vice versa. Names that are identical or nearly identical to an existing registered business name are not allowed.
You can, however, add an additional word to the name – in this example some additions are “consulting”, “international” or “enterprises”, to register the same name.
Do I Have To Register My Business Name With ASIC?
Yes.
Until 2012 business name registration was state based, but it has now moved to one national register managed through ASIC.
Because your business name is linked to an ABN, your business name contact details will also be searchable through the ABN register.
What Is The Difference Between A Trading Name And A Business Name?
A trading name refers to a name a business might use that is not currently registered. If you are using a trading name, or have used a trading name in the past and you want to continue using that name, then you should now register than name as your business name.
ABN Lookup will continue to display trading names until 31 October 2023. From 1 November 2023, ABN Lookup will not display trading names and will only display registered business names. What this means for your business is that anyone who checks ABN Lookup to ensure your business is legitimate is unlikely to find you unless you have a registered business name.
Business Name Registration Renewal
You don’t have to renew your business name registration every year. If you register through ASIC, you can register the business name for three years.
Provided you keep your contact details up to date, you will receive notice of renewal from ASIC before your registration expires. If you discover that your registration has expired, then you will still have 30 days after the registration date to apply to re-register that name before it becomes available to the public.
Business Name Registration Qld, NSW, Vic etc
Business name registration moved from a state based system to a national system back in 2012. If you had previously registered under the state system, your registration should have been migrated to the national ASIC register. Some registrations were lost in that process because people did not keep their details up to date.
If you lost your registration and someone else is now using that name, you may need to adjust your business name in order to get it registered again.
You don’t have any ownership rights in a business name. The purpose of registration is to identify who is behind a business and demonstrate the credibility of a business.
What Happens If My Business Name Is Not Registered?
Failing to register your business name, or to keep your registration up to date, can mean that someone else can register that business name and use it instead of you. If you allow your registration to lapse and someone else registers the same name, you have lost it and don’t have any automatic legal right to demand it back from the new business.
There may be a legal argument as to why they should hand it over, but to prove that right and get the order for them to handover the name, you would have to go through a court process. Court is costly, time consuming, stressful and provides no guarantee of success.
Can Someone Else Use My Business Name?
There are various legal arguments why someone else cannot use your business name without your permission. Whether you have an argument depends on all the circumstances, and we would need to have a discussion with you about your situation before advising.
Do I Own My Business Name?
Business name registration does not give you ownership rights. If you want the right to stop other people from using your business name, or something similar to your business name, then you may be better to register that name as a trade mark. Be aware that not all names are capable of achieving trade mark registration.
How can Onyx Legal help you?
Need help understanding your business name situation, or want to register your business name as a trade mark? Make an appointment with one of our team.





Recent Comments